What Is Trauma-Informed Care?
Trauma-informed care, or TIC, recognizes that trauma can negatively impact people of all ages. TIC encourages us to take into consideration a person’s past traumatic experiences.
What Is Trauma?
Trauma is a response to a deeply distressing or disturbing event that is difficult to cope with and can cause feelings of helplessness, a lack of self-awareness, and the inability to effectively process emotions and experiences.
Trauma can have lasting effects on your physical, mental, behavioral, social and/or spiritual well-being.
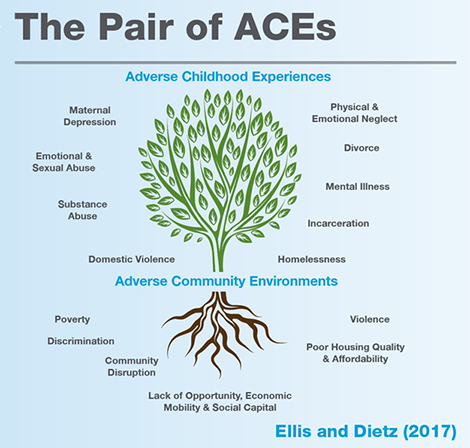
Examples of traumatic experiences are:
- Childhood neglect
- Living with a family member with mental health or substance use disorders
- Physical, sexual and emotional abuse
- Poverty
- Racism, discrimination and oppression
- Sudden separation from a loved one or death
- Violence in the community, war or terrorism
How Trauma Affects the Brain
Experiencing childhood trauma can change your brain structure, resulting in long-term physical and behavioral health problems. Experiencing trauma causes your body to produce cortisol and adrenaline, which activate your body’s processes of fight, flight or freeze.
The Effects of Trauma on Health
The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) study shows that when a child is exposed to adverse childhood experiences, they are at greater risk for chronic health conditions and risky behaviors.
The ACE study asked people to indicate the number of traumatic events they’ve experienced prior to the age of 18. It also provides an “ACE score” that consists of the sum of each traumatic experience question answered with “yes." Compared to people who scored a zero on this self-assessment, individuals with an ACE score of 4 or more were approximately:
- 2x as likely to smoke
- 2.5x more likely to have sexually transmitted diseases
- 4x more likely to have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 7x more likely to consider themselves an alcoholic
- 10x as likely to have injected street drugs
- 12x as likely to have attempted suicide
The Importance of Being Trauma-Informed
Being trauma-informed should be the standard, not the exception. Using trauma-informed approaches in work, family, community and everyday life can positively impact the lives of everyone involved.